A background task manager is the unsung hero of a smooth mobile app. It’s the system working diligently behind the scenes, handling heavy-duty jobs so your app’s interface stays quick and responsive. Think of it as a smart assistant that downloads files, syncs data, or crunches numbers without ever getting in the user’s way.
What Is a Background Task Manager

Let’s use an analogy. Imagine your app is a busy restaurant. The main thread is the waiter out front, taking orders and interacting with customers—this is your user interface (UI). If that same waiter had to run to the kitchen to cook every single meal, the entire dining room would grind to a halt.
A background task manager is your kitchen crew. They handle all the complex preparation and cooking in the back, letting the waiter provide seamless, uninterrupted service. This separation is what keeps the restaurant running smoothly.
Without this division of labor, a long-running task like uploading a high-resolution video would completely freeze the app. The user would be stuck staring at a frozen screen, unable to do anything until the upload finishes. That’s a recipe for a bad review.
Why Background Processing Is Essential
A background task manager is the solution to several critical problems that can seriously degrade an app’s quality.
Here’s what it brings to the table:
- No More UI Freezes: It moves processor-intensive tasks off the main thread, which means the app’s interface remains fluid and interactive at all times.
- Instant Responsiveness: Users get immediate feedback because the UI is never blocked by a hidden process chugging away in the background.
- Smart Resource Management: It can schedule jobs intelligently, waiting to run them when the device has a stable network connection or sufficient battery life.
To better understand how this all works, it’s helpful to look at the difference between synchronous and asynchronous communication, a core concept in modern app development.
Essentially, a background task manager lets you schedule work to happen later or in parallel. You could set up a recurring task to check for new content, a technique that also powers features like seamless over-the-air updates.
The table below breaks down the primary responsibilities of a background task manager and illustrates the direct impact each has on the end-user.
Core Functions of a Background Task Manager
| Function | Description | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Offloading Heavy Tasks | Moves long-running operations (e.g., file processing, API calls) away from the main UI thread. | The app remains responsive and interactive, eliminating frustrating freezes and lag. |
| Scheduling and Deferral | Allows tasks to be scheduled for a later time or when certain conditions are met (e.g., device charging). | Optimizes battery life and data usage, making the app a better citizen on the user’s device. |
| Data Synchronization | Keeps local data in sync with a remote server without interrupting the user’s workflow. | Users always have the most up-to-date information without manual refreshes or waiting. |
| Resilience and Retries | Automatically retries failed tasks (like a failed upload) with strategies like exponential backoff. | Ensures critical operations eventually succeed, even with intermittent network connectivity. |
By managing these functions, the task manager ensures that no matter what’s happening behind the curtain, the show goes on for the user without a hitch.
How Mobile Operating Systems Keep Background Tasks in Check
Think of your phone’s operating system—iOS or Android—as a strict bouncer at an exclusive club. Its main job is to protect the device’s precious resources, like battery and processing power. It can’t let every app run wild in the background; that would drain the battery in no time and bring the whole system to a crawl.
To keep things running smoothly, the OS puts every app through a clear lifecycle. An app is usually in one of three states:
- Active: You’re using it right now. It’s on your screen, front and center.
- Background: You’ve switched to another app, but your app gets a tiny window of time to quickly finish up what it was doing.
- Suspended: The app is basically frozen in memory. It’s not running any code, which is how the OS saves power.
That jump from active to background is where the OS really lays down the law. Your app has a very short, limited time to get its work done before it’s put on ice.
Working Within Each OS’s Rules
Every operating system has its own way of managing this process. On iOS, developers used to rely on older APIs like Background Fetch. But since iOS 13, the go-to tool has been the BGTaskScheduler framework, which is much smarter about scheduling things like refreshing your feed or cleaning up a local database. To see how these rules play out in a real project, you can check out this detailed guide on setting up an iOS background task.
Android, on the other hand, gives developers a powerful and flexible library called WorkManager. It’s the standard for any background work that needs to get done but doesn’t have to happen right now. WorkManager is clever—it considers things like the phone’s battery level and whether it’s on Wi-Fi before deciding the best moment to run a task.
No matter the platform, the golden rule is the same: the operating system always has the final say on when—or if—a background task runs. This is non-negotiable, and it’s what guarantees a good, consistent experience for the user.
When you use a background task manager in React Native, it’s essentially acting as a translator, smoothing over these platform-specific differences with a single, unified API. Still, knowing what’s happening under the hood on both iOS and Android is key to building background features that actually work reliably without frustrating users or getting shut down by the OS.
Implementing Background Tasks in React Native
So, how do we translate all that platform-specific theory into actual code for a React Native app? Thankfully, we don’t have to wrestle with iOS’s BGTaskScheduler and Android’s WorkManager directly. The community has built some fantastic libraries that create a bridge, giving us a single, clean JavaScript API to work with.
One of the go-to tools for this is react-native-background-fetch. It’s perfect for scheduling tasks that need to run every so often when the app is closed. Think of it as a way to quietly sync user data or refresh a content feed without needing the user to open the app. It’s built for those non-urgent, “nice-to-have” updates.
This infographic gives a great visual of how a mobile app moves between being active, in the background, and eventually suspended by the operating system.
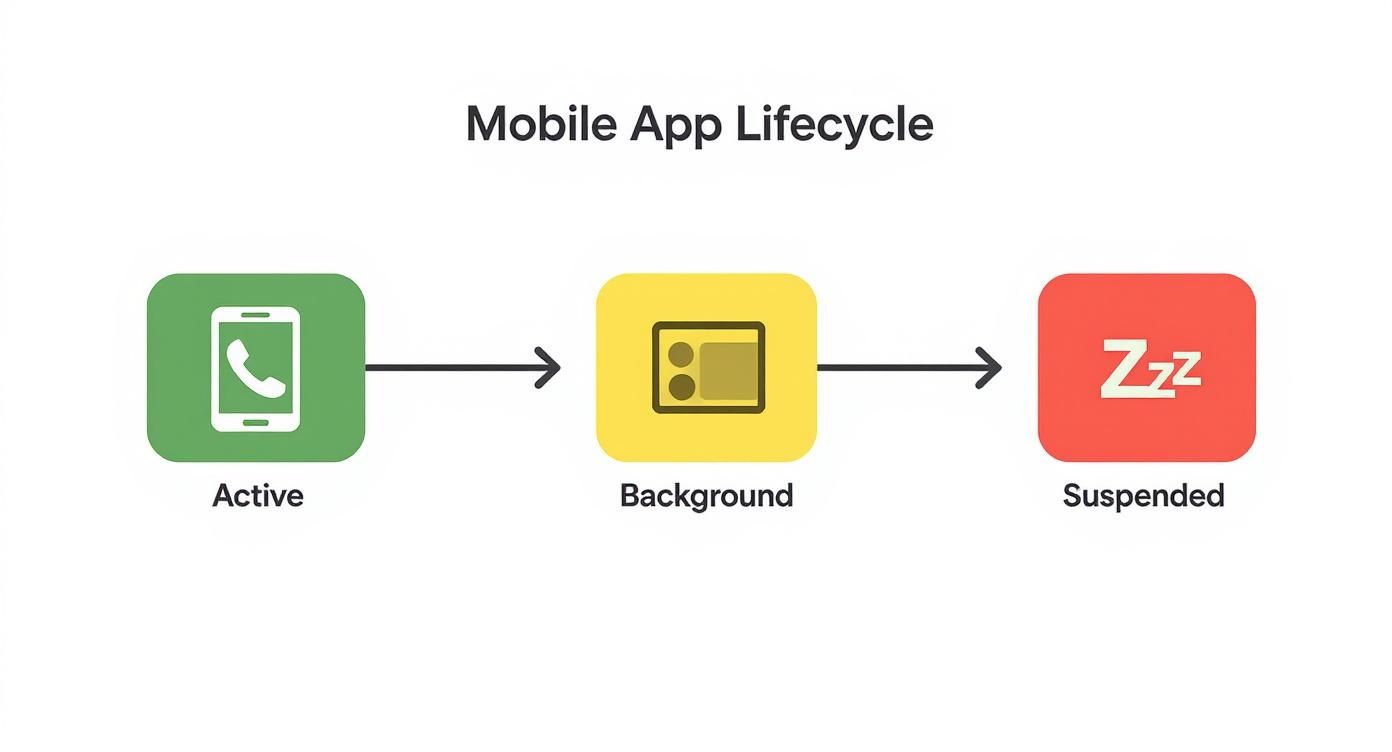
The main thing to remember is that your app gets a very short window of time to do its work in the background. After that, the OS will put it to sleep to save power.
A Practical Example
Let’s walk through a common scenario: setting up a recurring task to sync app data every 30 minutes. With a library, the process is pretty straightforward and breaks down into three main steps.
- Configuration: First, you tell the task manager how you want it to behave, primarily by setting the minimum time between runs. Remember, this is more of a suggestion to the OS, not a strict guarantee.
- Event Listener: This is where your actual code goes. You set up a listener for the “fetch” event, and inside it, you might make an API call or update a local database.
- Task Completion: This part is absolutely critical. You must tell the operating system when your task is done. If you forget this step, the OS might think your app is misbehaving and penalize it by limiting its background time in the future.
Following this structure keeps your background tasks playing by the rules, which is essential for preserving battery life and device performance. The demand for this kind of automation is exploding; the task management agent market is on track to hit USD 17.9 billion by 2034. This number really highlights how much businesses rely on tools that can handle automated processes behind the scenes.
A well-implemented background task feels invisible to the user but delivers immense value. The best background processes provide fresh data and seamless updates without ever drawing attention to themselves or draining the battery.
Getting these tasks to run smoothly depends on a solid grasp of how JavaScript and native code communicate. If you want to get a better handle on that connection, our guide on how React Native modules work is a great place to start. It’s foundational knowledge for anyone serious about debugging and optimizing background services.
Powerful Use Cases for Background Processing
https://www.youtube.com/embed/7J-ilYJqh9U
The real magic of a background task manager isn’t in the code itself, but in the seamless experiences it creates. These silent workers are the unsung heroes behind the apps we love, solving problems before we even know we have them.
Think about your favorite news app. When you open it, the latest headlines are already there, right? That’s not an accident. A background task likely fetched that new content an hour ago, so you never have to sit through a loading screen. It just works.
Enhancing App Functionality
This “get it ready ahead of time” approach is what separates a clunky app from a great one. It lets developers build features that would otherwise be frustrating or completely impractical.
-
Large File Uploads: Ever uploaded a high-res video to a social app? A background task lets you hit “upload,” then go back to browsing your feed. It handles the heavy lifting without freezing the app or forcing you to stare at a progress bar.
-
Location Tracking: Fitness apps need to track your run even if you lock your phone and put it in your pocket. That’s a background task, reliably logging your route and distance without needing the app to be front and center.
-
Data Pre-fetching: Music streaming services use background tasks to download the next few songs in your playlist. This is why your music keeps playing smoothly, even when you drive through an area with a spotty connection.
The best background tasks are completely invisible. You don’t see them working; you just notice that the app feels fast, fresh, and always ready for you.
This kind of proactive, behind-the-scenes work is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s what users expect. It’s a big reason why the task management software market, valued at around USD 1.27 billion in 2025, is expected to skyrocket to USD 3.26 billion by 2030. You can dig deeper into these market trends on mordorintelligence.com. This growth is all about the rising demand for apps that feel smart and responsive.
Best Practices for Efficient Background Tasks
Adding a background task manager to your app is a game-changer, but get it wrong, and you can create a nightmare of battery drain and user frustration. The trick is to build tasks that are helpful, not resource hogs. Your goal is to be a good citizen on the user’s device.
First things first: schedule tasks intelligently. Don’t just run tasks constantly. Ask yourself, does your app really need to sync data every five minutes, or would once an hour do the job? Every single time a task runs, it sips a bit of battery, so always go for the longest interval that still makes sense for the user experience. A great pro-tip is to schedule non-essential updates for when the device is charging or connected to Wi-Fi.
You also have to handle network changes gracefully. A user’s connection can be flaky at best. Your background task should always check if there’s a solid network connection before trying to hit an API. If that connection drops halfway through, your code needs to handle it smoothly—maybe by scheduling a retry for later instead of getting stuck in a frustrating loop.
Optimizing Resource Usage and Reliability
Beyond just scheduling, you have to think about managing resources and planning for failure. When you’re architecting your background tasks, really digging into the differences between batch vs stream processing is key. This choice directly impacts how you handle data and can make a massive difference in your app’s overall efficiency.
And don’t forget to provide clear user feedback for long-running operations. If your app is downloading a huge file in the background, a simple, non-intrusive notification showing the progress goes a long way. It keeps the user in the loop and stops them from thinking your app is just frozen.
If there’s one thing to get right, it’s robust error handling and monitoring. A background task should never, ever fail silently. Set up comprehensive logging and use the right tools to keep an eye on performance, just like the ones covered in these application performance monitoring best practices.
Finally, test relentlessly. Background behavior is notoriously inconsistent across different devices, OS versions, and even battery levels. A task that runs like a dream on a brand-new flagship phone might completely fall apart on an older, low-battery device. The only way to ensure your background processes are solid for everyone is to test them in as many real-world scenarios as you can.
Automating Updates with CodePushGo

When you pair a background task manager with an Over-the-Air (OTA) update service like CodePushGo, you create a powerhouse for keeping your app fresh. Instead of making users trudge back to the app store, you can push crucial updates quietly and efficiently behind the scenes.
This completely changes the update game. What was once a disruptive, manual chore for the user becomes an invisible, automatic process. The concept is straightforward: set up a recurring background task that simply checks to see if a new version of your app is available.
If an update is found, the background task can download it without interrupting what the user is doing or burning through their mobile data at a bad time. The new code is then stored safely on the device, ready to go the very next time the app opens.
The Power of Silent Updates
This combination is a win-win for everyone. As a developer, you get to ship bug fixes and new features almost instantly, skipping the often unpredictable app store review queues.
The advantages are hard to ignore:
- Faster Bug Fixes: You can squash critical bugs in minutes, not days.
- Non-Disruptive Experience: Users never get that annoying “Update Required” pop-up that forces them to stop and download something.
- Improved Adoption: This approach ensures a much higher percentage of your users are always on the latest version, which makes support and maintenance a whole lot easier.
It’s a hands-off strategy that guarantees your users have the best version of your app without even thinking about it. This is a perfect example of a background process creating a smoother, more reliable experience that builds real trust.
Putting it all together means configuring a background job to ping your CodePushGo deployment every so often. If the check finds a new package, it triggers the download. For a deeper dive into the mechanics, you can explore this guide on deploying a React Native app with CodePushGo.
What you end up with is a fully automated delivery pipeline. This proactive approach keeps your app secure, stable, and packed with the latest features—all handled silently by your background task manager.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers
When you start working with background tasks, a few common questions always pop up. Let’s tackle them head-on so you can build with confidence.
How Often Should a Background Task Actually Run?
This really boils down to your specific needs, but the best advice is to be mindful of the user’s battery. Think less, not more.
For things like non-urgent data syncing, aiming for an interval anywhere between 30 minutes to a few hours is a good starting point. Keep in mind that both Android and iOS have their own rules to prevent abuse, often setting a minimum frequency of around 15 minutes. Trying to run tasks more frequently than that is a surefire way to drain the battery and get your app restricted by the OS.
What Should I Do If a Background Task Fails?
First thing’s first: a background task should never fail silently. Your code needs solid error handling to catch these hiccups.
When a failure happens, log it. If the task is critical, you’ll want to build in a retry strategy, but do it smartly. A common approach is an exponential backoff—if a network call fails, wait a minute, then two, then four, and so on. Just be sure to cap the retries to avoid a never-ending loop that, once again, kills the battery.
One crucial thing to remember: a background task runs on a completely different thread from your app’s user interface. This means it can’t directly change what the user sees on the screen. The right way to communicate is by sending an event that the UI can listen for, ensuring any visual updates happen safely on the main thread.
Ready to take the next step and automate your app updates in the background? CodePushGo works perfectly with background task managers to deliver seamless, silent updates. Your users get the latest features without any interruption.
Get started with CodePushGo and keep your app effortlessly up-to-date.




